Tools Selection Skills of CNC Machining

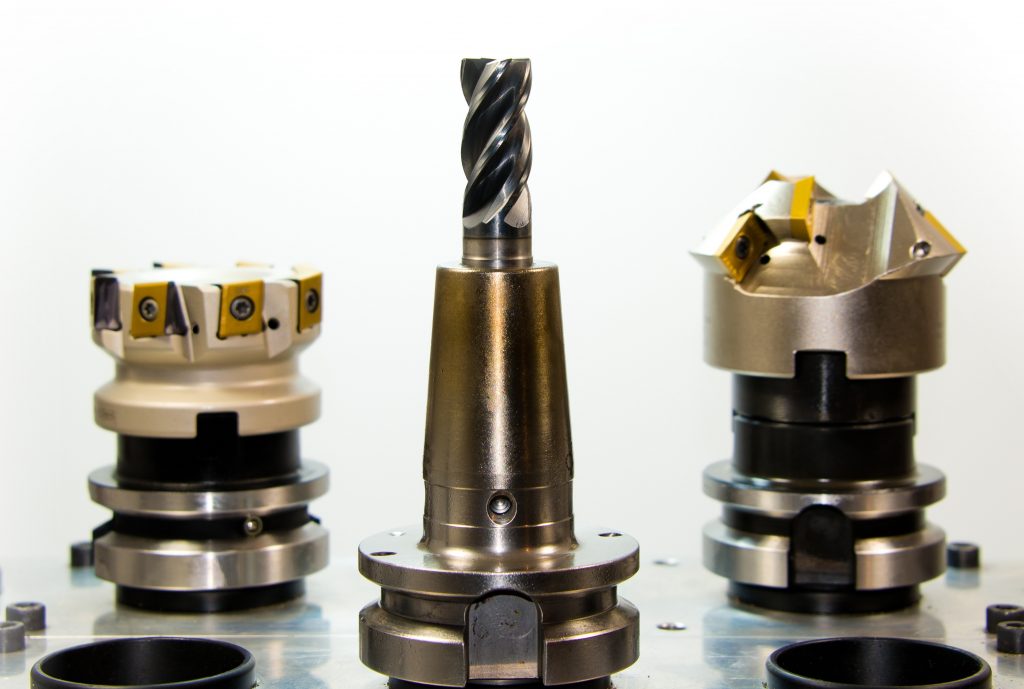
Choose Tools for CNC Milling
In CNC machining, flat-bottomed end mills are commonly used for milling the inner and outer contours of plane parts and the milling plane. The empirical data of the relevant parameters of the tool are as follows: First, the radius of the milling cutter should be smaller than the minimum radius of curvature Rmin of the inner contour surface of the part, generally RD= (0.8-0.9) Rmin. The second is the processing height of the part H< (1/4-1/6) RD to ensure that the knife has sufficient rigidity. Third, when milling the bottom of the inner groove with a flat-bottomed end mill, because the two passes of the groove bottom need to be overlapped, and the radius of the bottom edge of the tool is Re=Rr, that is, the diameter is d=2Re=2(Rr), when programming Take the tool radius as Re=0.95 (Rr).
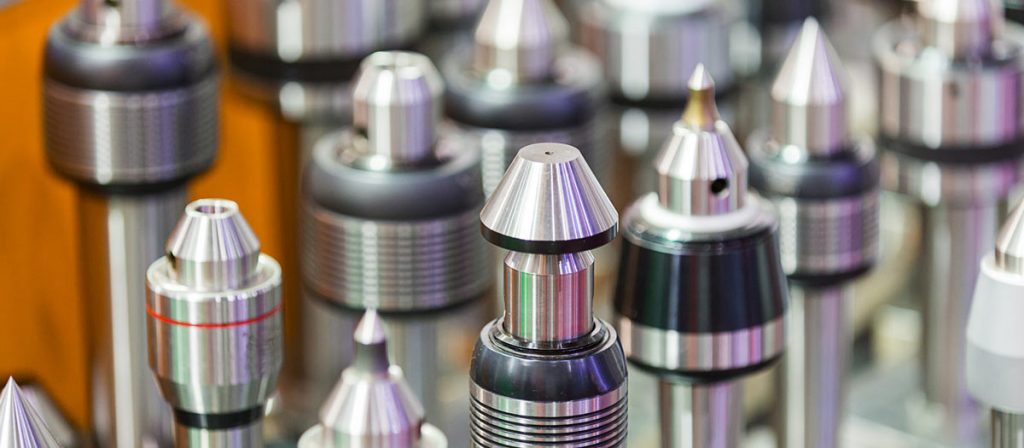
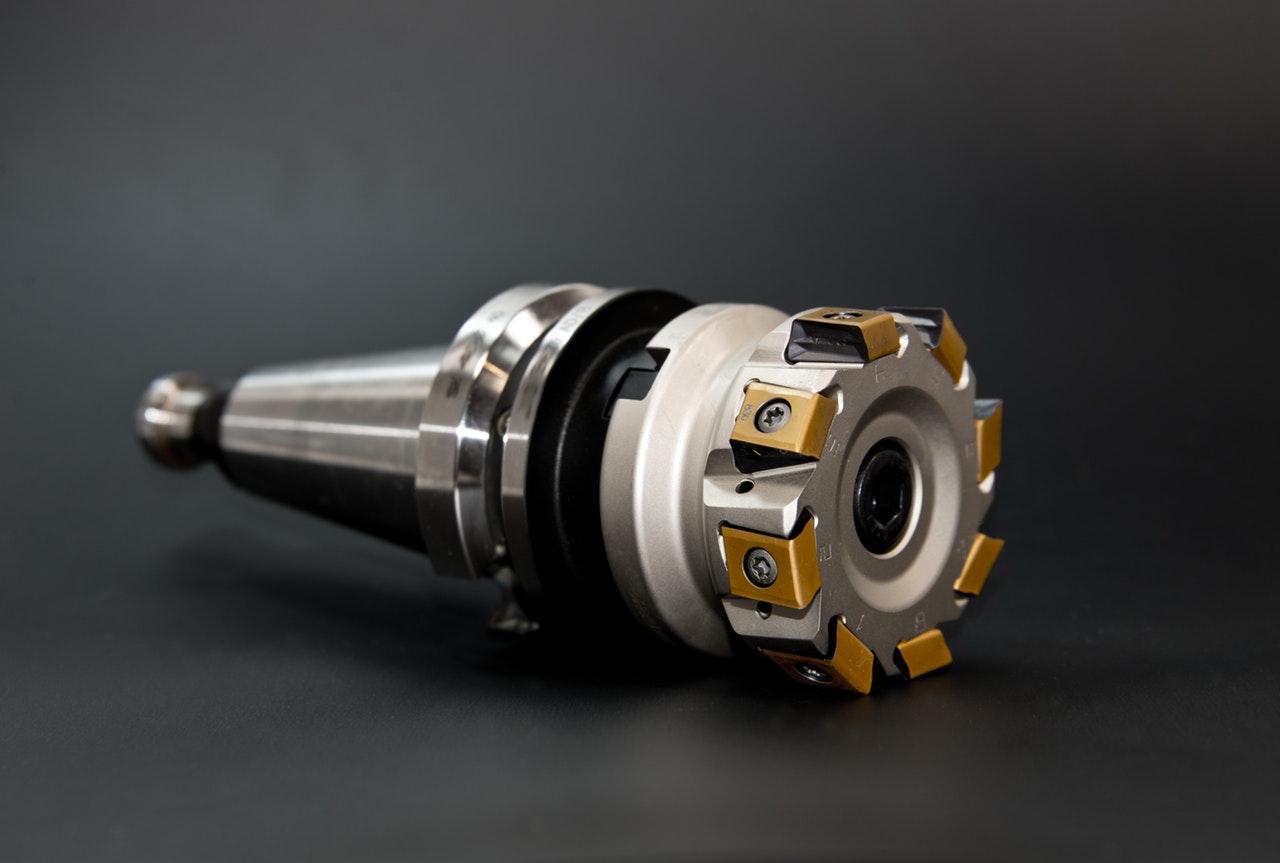
For the processing of some three-dimensional profiles and contours with variable bevel angles, spherical milling cutters, ring milling cutters, drum milling cutters, tapered milling cutters and disc milling cutters are commonly used. At present, most of the CNC machine tools use serialized and standardized tools. There are national standards and serialized models for tool holders and tool heads such as indexable machine-clamped external turning tools and face turning tools. For machining centers and automatic tool changers The installed machine tools and tool holders have been serialized and standardized. For example, the standard code of the tapered shank tool system is TSG-JT, and the standard code of the straight shank tool system is DSG-JZ. In addition, for the selected tool Before use, it is necessary to strictly measure the tool size to obtain accurate data, and the operator will input these data into the data system, and complete the processing process through the program call, thereby processing qualified workpieces.


Folding Tool Point and Tool Change Point
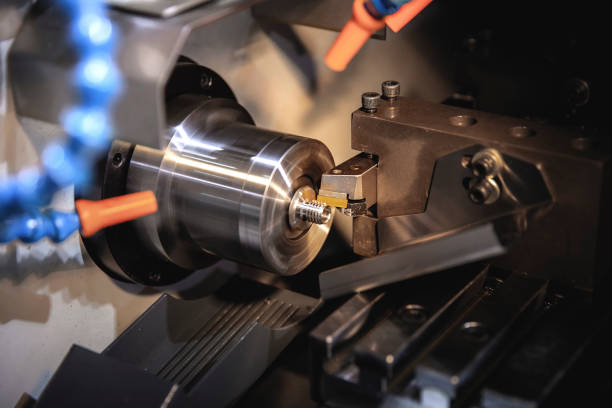
From what position does the tool start to move to the specified position? So at the beginning of the program execution, the position where the tool starts to move in the workpiece coordinate system must be determined. This position is the starting point of the tool relative to the workpiece when the program is executed. So it is called the program starting point or starting point. This starting point is generally determined by tool setting, so this point is also called tool setting point. When compiling the program, the position of the tool setting point must be selected correctly. The principle of tool setting point setting is to facilitate numerical processing and simplify programming.
It is easy to align and check during processing; the processing error caused is small. The tool setting point can be set on the machined part, on the fixture or on the machine tool. In order to improve the machining accuracy of the part, the tool setting point should be set as far as possible on the part's design reference or process base. In actual operation of the machine tool, the tool position point of the tool can be placed on the tool setting point by manual tool setting operation, that is, the coincidence of the "tool position point" and the "tool setting point". The so-called "tool location point" refers to the positioning datum point of the tool, and the tool location point of the turning tool is the tool tip or the center of the tool tip arc.
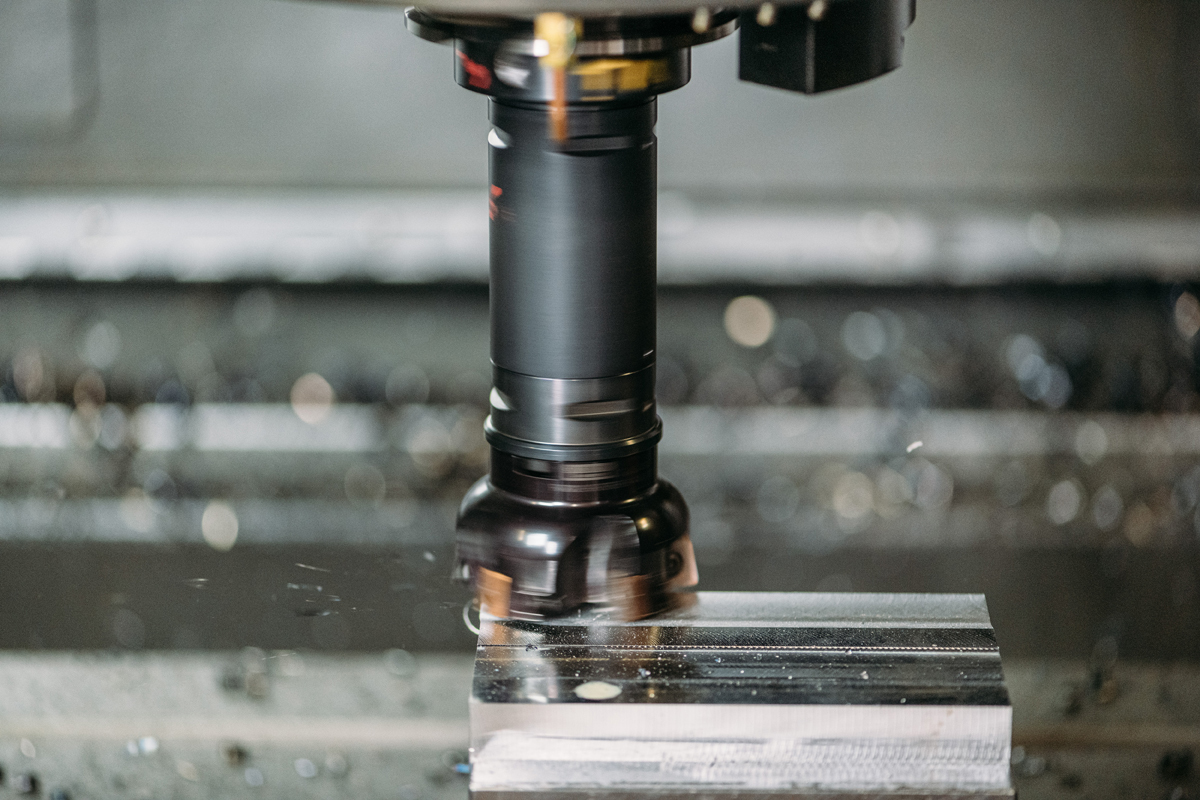


The flat-bottomed end mill is the intersection of the tool axis and the bottom of the tool; the ball-end mill is the center of the ball, and the drill is the point. Using manual tool setting operation, the tool setting accuracy is low, and the efficiency is low. Some factories use optical tool setting mirrors, tool setting instruments, automatic tool setting devices, etc. to reduce tool setting time and improve tool setting accuracy. When the tool needs to be changed during processing, the tool change point should be specified. The so-called "tool change point" refers to the position of the tool post when it rotates to change the tool. The tool change point should be located outside the workpiece or fixture, and the workpiece and other parts should not be touched during the tool change.
The tip of this type of turning tool is composed of linear main and secondary cutting edges, such as 900 internal and external turning tools, left and right end face turning tools, grooving (cutting) turning tools, and various external and internal cutting edges with small tip chamfers. Hole turning tool. The selection method of the geometric parameters of the pointed turning tool (mainly the geometric angle) is basically the same as that of ordinary turning, but the characteristics of CNC machining (such as machining route, machining interference, etc.) should be considered comprehensively, and the tool tip itself should be considered strength.
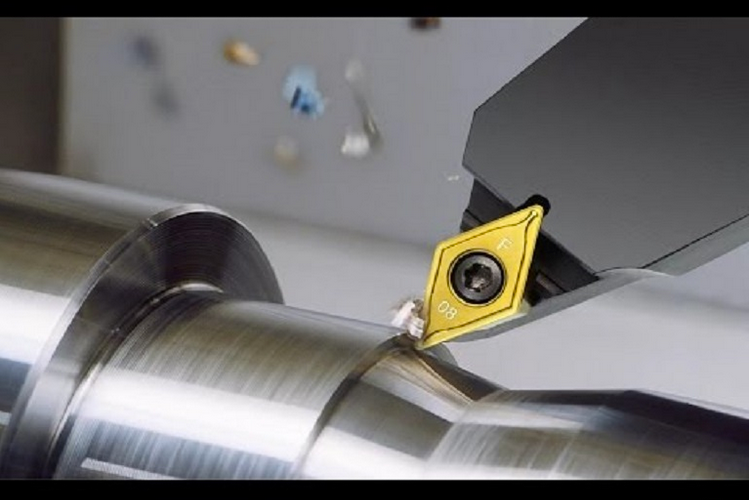
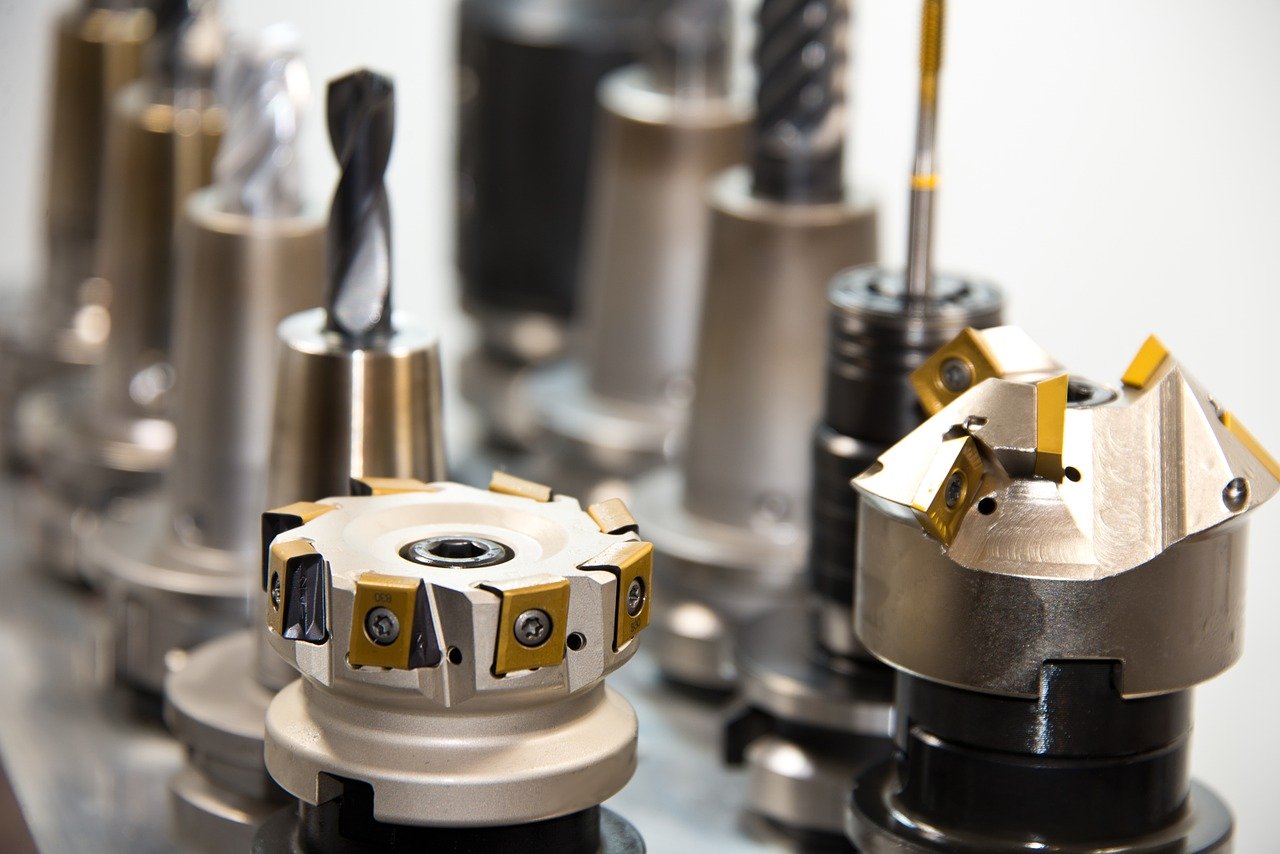
Determine Cutting Amount
In NC programming, the programmer must determine the cutting amount of each process and write it in the program in the form of instructions. Cutting parameters include spindle speed, back-cutting amount and feed speed. For different processing methods, different cutting parameters need to be selected. The selection principle of the cutting amount is to ensure the machining accuracy and surface roughness of the parts, give full play to the cutting performance of the tool, ensure reasonable tool durability, and give full play to the performance of the machine tool to maximize productivity and reduce costs.















