Mechanical Machining Types

Main Classification
There are two main types of machining: manual machining and CNC machining. Manual processing refers to the method of processing various materials by manual operation of mechanical equipment such as milling machines, lathes, drilling machines and sawing machines by mechanical workers. Manual machining is suitable for low-volume, simple part production. CNC machining (CNC) refers to the use of CNC equipment by mechanical workers for processing. These CNC equipment includes machining centers, turning and milling centers, wire EDM equipment, thread cutting machines, etc. The vast majority of machine shops use CNC machining technology. Through programming, the position coordinates (X, Y, Z) of the workpiece in the Cartesian coordinate system are converted into programming language.
The CNC controller of the CNC machine tool controls the axis of the CNC machine tool by identifying and interpreting the programming language, and automatically removes materials as required. , so as to obtain the finished workpiece. CNC machining processes workpieces in a continuous manner and is suitable for large quantities of parts with complex shapes.
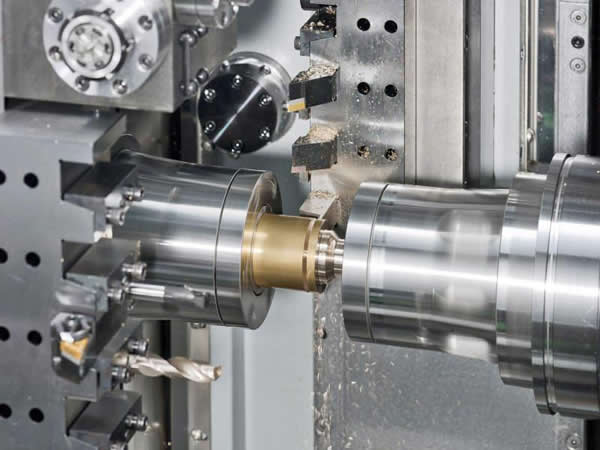


Processing Technology
The machining workshop can use CAD/CAM (Computer Aided Design Computer Aided Manufacturing) system to automatically program the CNC machine tools. The geometry of the part is automatically transferred from the CAD system to the CAM system, and the machinist selects various machining methods on a virtual display. When the machinist selects a certain machining method, the CAD/CAM system can automatically output the CNC code, usually referred to as the G code, and input the code into the controller of the CNC machine tool for actual machining operations.
Other Equipment
Equipment behind the factory, such as metal cutting machine tools (including turning, milling, planing, inserting and other equipment), if the parts of the equipment required for production are broken and need to be repaired, they need to be sent to the machining workshop for repair or processing. In order to ensure the smooth progress of production, general enterprises have machining workshops, which are mainly responsible for the maintenance of production equipment.
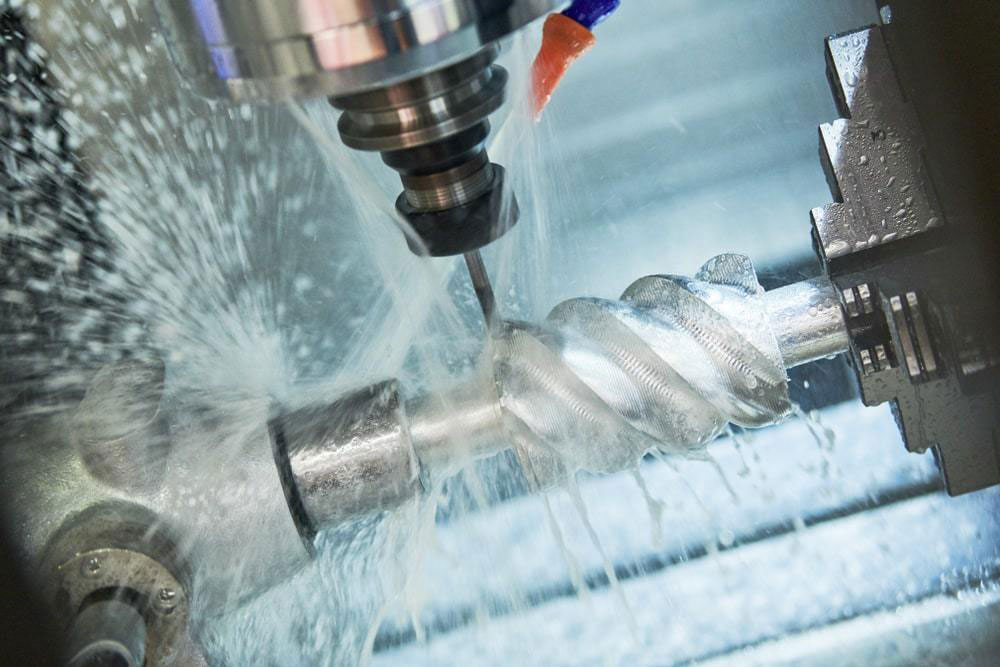


Operating Procedures
I. Overview
This operating procedure makes specific and detailed instructions for all operators engaged in machining to ensure the quality of each machined part.
2. Scope of application
This regulation specifies the specific operations of machining personnel (including turning, milling, drilling, planing, grinding, shearing, etc.) during work.
3. General rules
Mechanical processing must be carried out in accordance with this regulation during the processing of various machine parts.
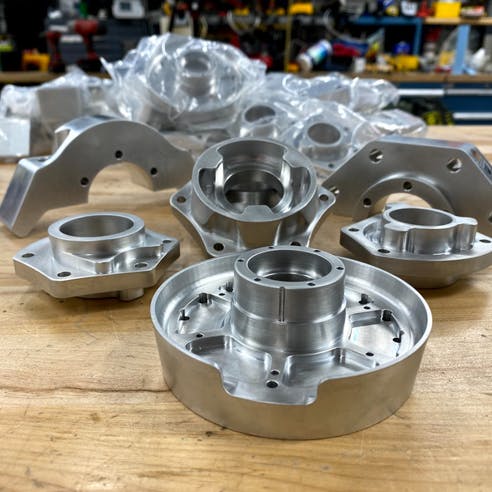
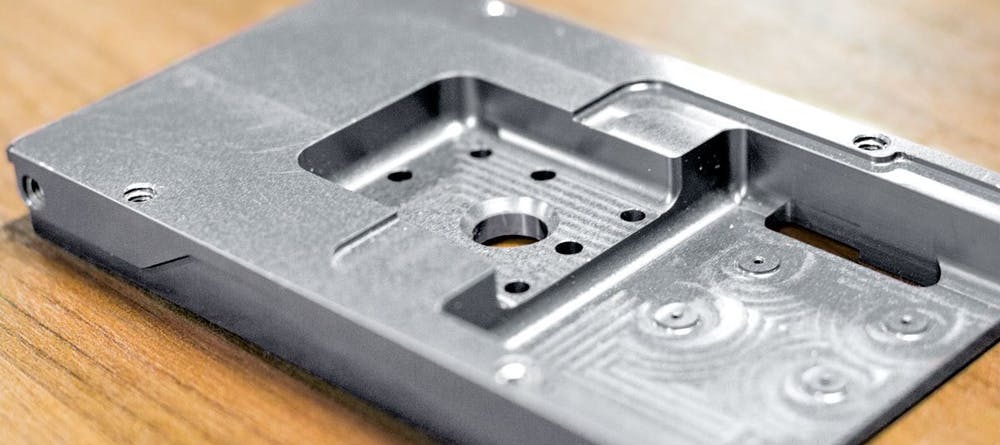



Send your message to us:
-

Aluminum CNC Machining Parts
-

Aluminum Sheet Metal Fabrication
-

Axis High Precision CNC Machining Parts
-

CNC Machined Parts for Italy
-

CNC Machining Aluminum Parts
-

Auto Parts Machining
-

Titanium Alloy Forgings
-

Titanium and Titanium Alloy Fittings
-

Titanium and Titanium Alloy Forgings
-

Titanium and Titanium Alloy Wires
-

Titanium Bars
-

Titanium Seamless Pipes/Tubes
-

Titanium Welded Pipes/Tubes