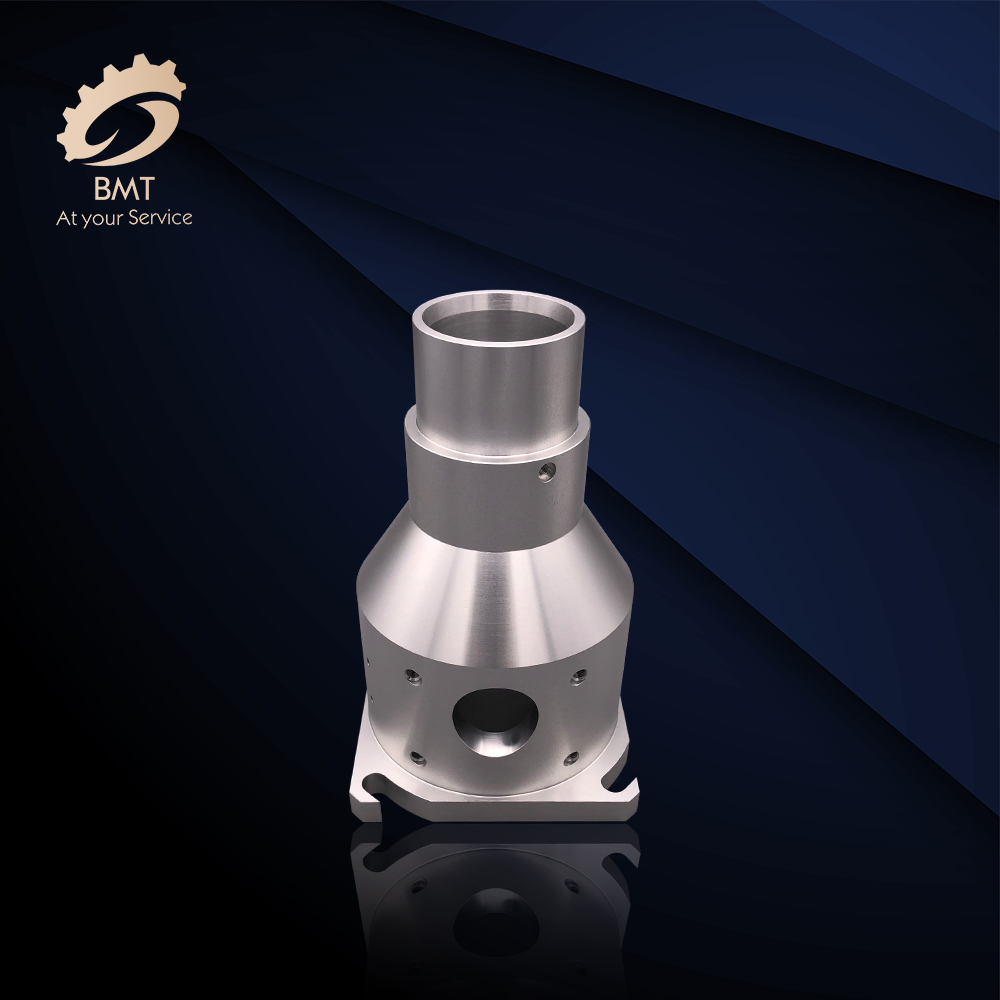
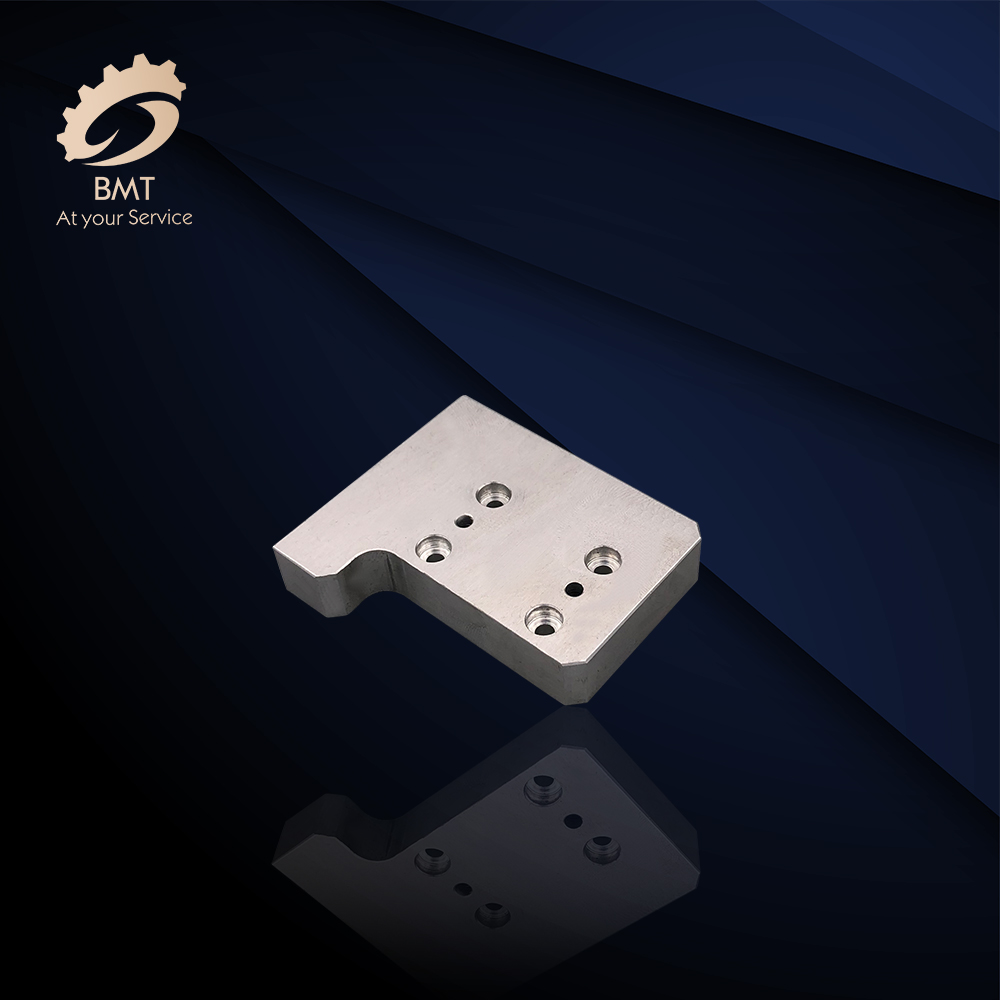
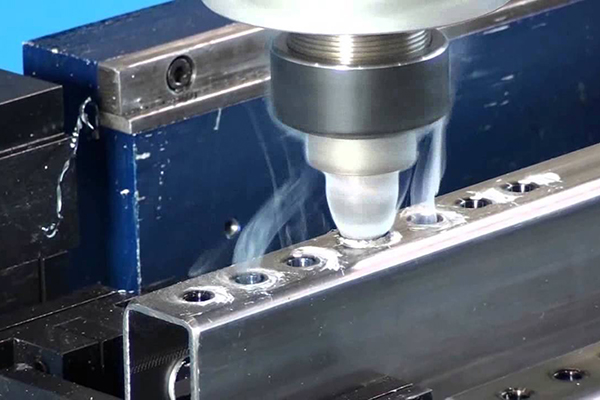
Types of CNC Machining Operations
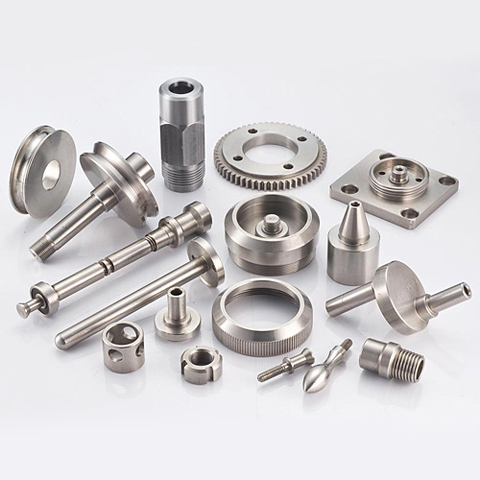
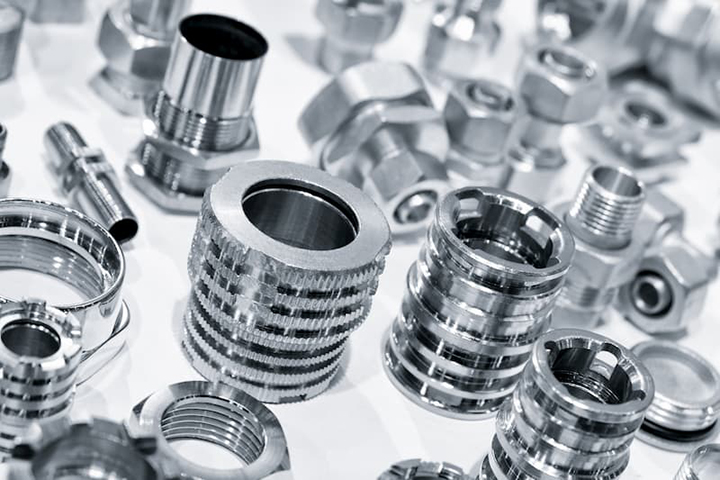
CNC machining is a manufacturing process, which is suitable for a wide variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and agriculture, etc. It is able to produce a wide range of products, such as automobile parts, surgical equipment parts, food industry equipment parts, airplane parts, or even home appliance parts, etc. This process includes several different computer controlled machining operations to remove the material from the workpiece and to produce a custom-designed part. Some processes, like chemical, electrical and thermal machining will be covered after mechanical machining, like anodizing, electroplating, zinc plating, etc.
The most common mechanical CNC machining operations including:
▶ CNC Turning
▶ CNC Drilling
▶ CNC Milling
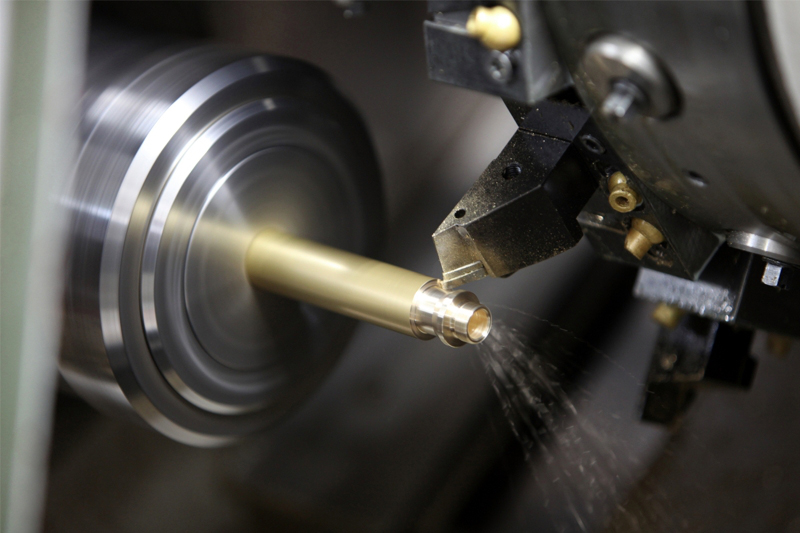
CNC Turning
Turning is a kind of machining process which uses single-point cutting tools to remove material from the rotating workpiece on lathe machine. In CNC turning, normally we call it lathe machine or turning machine, removing material around the circumference until the desired diameter is achieved, to produce cylindrical parts with internal and external features, such as grooves, slots, tapers, and threads. Operational capabilities of the turning process include boring, facing, grooving and thread cutting.
CNC Drilling
Drilling is a machining process which employs
Drilling is a process of making cylindrical holes on the workpiece with multi-point drill bits. In CNC drilling, the CNC Machines make the perpendicularly to the workpiece surface with rotating drill bit which produces vertically-aligned holes with diameters equal to the diameter of the drill bit for the drilling operation. However, angular drilling operation can be also performed using specialized machine configurations and working fixtures. The operational capabilities of the drilling process include counter boring, counter sinking, reaming and tapping.

CNC Milling
Milling is a machining process which employs rotating multi-point cutting tools to remove material from the workpiece. In CNC Milling, the CNC machine typically feeds the workpiece to the cutting tool in the same direction as the cutting tool’s rotation, whereas, in manual milling, the machine feeds the workpiece in the opposite direction to the cutting tools’ rotation. Operational capabilities of the milling process include face milling and peripheral milling, including cutting shallow, flat surface and flat-bottomed cavities into the workpiece as well as cutting deep cavities of slots and threads into workpiece.
Sum up, Characteristics of Common CNC Machining Operations are illustrated here:
|
Machining Operation |
Characteristics |
|
Turning |
Employs single-point cutting tools Rotates workpiece Cutting tool fed along the surface of the workpiece Removes material from the workpiece Produces round or cylindrical parts |
|
Drilling |
Employs rotating multi-point drill bits Drill bit fed perpendicular or angularly to workpiece Produces cylindrical holes in workpiece |
|
Milling |
Employs rotating multi-point cutting tools Workpiece fed in same direction as cutting tool rotation Removes material from workpiece Produces broader range of shapes |