Grinding Processing

Grinding processing belongs to finish machining (machining is divided into rough machining, finish machining, heat treatment and other processing methods), with less processing amount and high precision. It is widely used in the machinery manufacturing industry. The heat treated and quenched carbon tool steel and carburized and quenched steel parts often have a large number of regularly arranged cracks - grinding cracks - on the surface that is basically perpendicular to the grinding direction during grinding. It not only affects the appearance of the parts, but also directly affects the quality of the parts.
It refers to the cutting process of workpiece surface with high-speed rotating grinding wheel and other abrasive tools. Grinding is used to process internal and external cylindrical surfaces, conical surfaces and planes of various workpieces, as well as special and complex formed surfaces such as Ge Ban chips, threads, gears and splines.


Due to the high hardness of abrasive grains and the self-sharpening of abrasive tools, grinding can be used to process various materials, including hardened steel, high-strength alloy steel, hard alloy, glass, ceramics, marble and other high hardness metal and non-metallic materials. The grinding speed refers to the linear speed of the grinding wheel, which is generally 30~35 m/s. If it exceeds 45 m/s, it is called high-speed grinding.
Grinding is usually used for semi finishing and finishing, and the accuracy can reach IT8~5 or even higher. The surface roughness is generally ground to Ra1.25~0.16 μ m, precision grinding to Ra0.16~0.04 μ m, ultra precision grinding to Ra0.04~0.01 μ m, and mirror grinding to Ra0.01 μ m. The specific power of grinding (or specific energy consumption, that is, the energy consumed to cut the workpiece material per unit volume) is larger than that of general cutting, and the metal removal rate is smaller than that of general cutting.
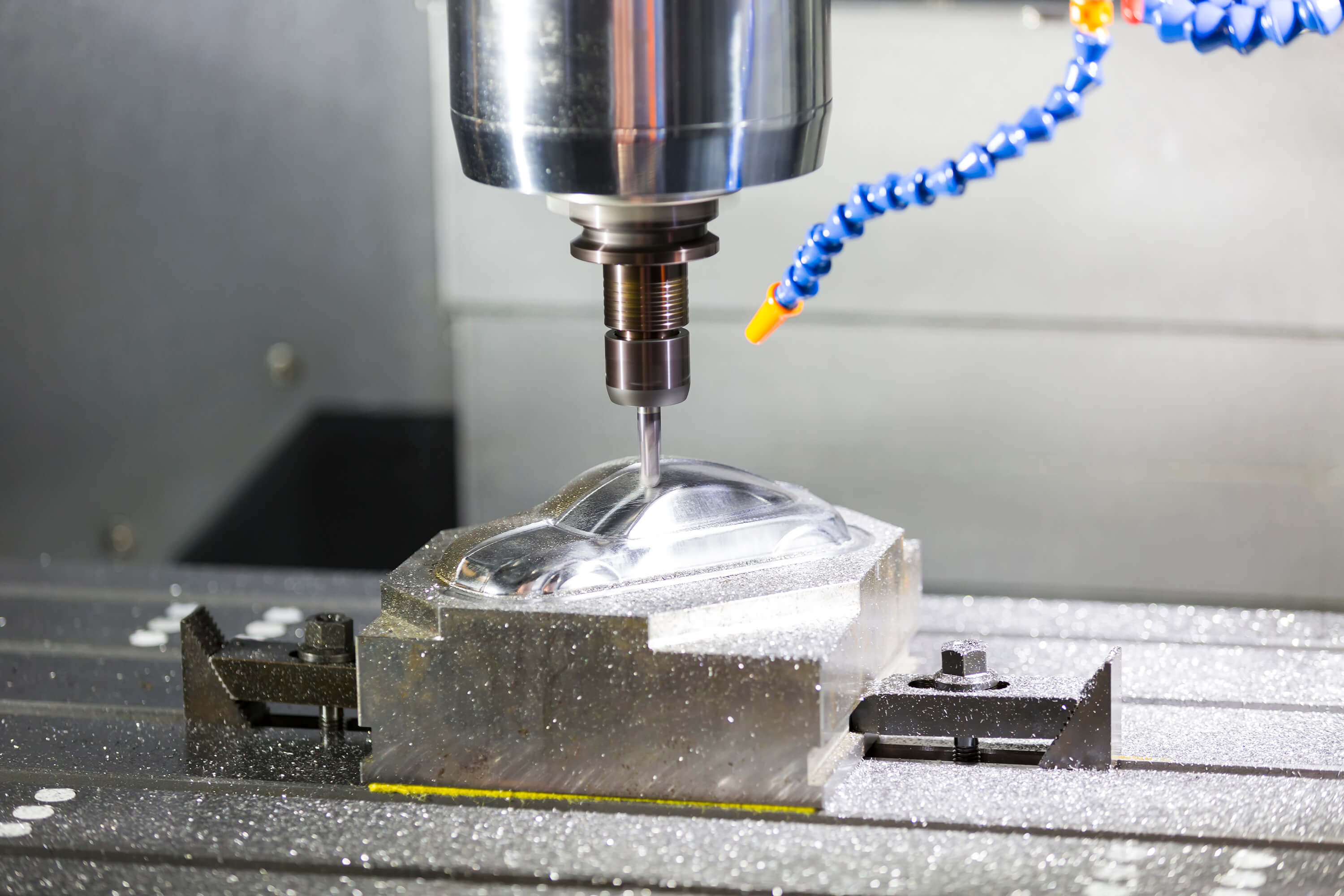
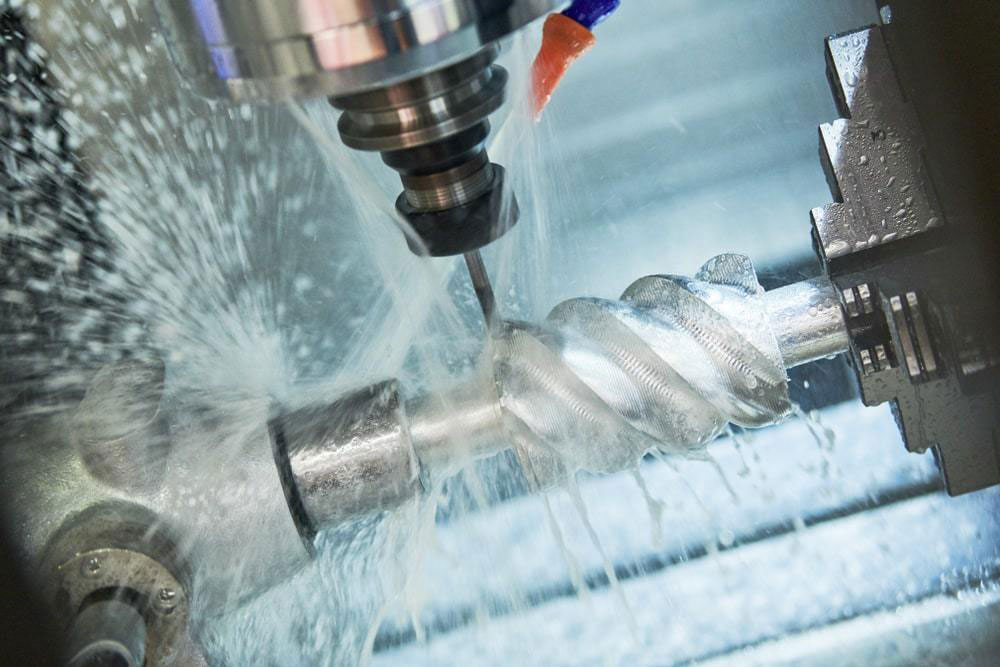


Therefore, before grinding, the workpiece is usually removed by other cutting methods to remove the machining allowance of major parts of Jiang Ali, leaving only 0.1~1mm or less of the grinding allowance. With the development of high efficiency grinding, such as creep feed grinding and high speed grinding, parts can be ground directly from blanks. It can also be used for rough machining by grinding, such as removing the runner and riser of castings, the flash of forgings and the skin of steel ingots.



Send your message to us:
-

Aluminum CNC Machining Parts
-

Aluminum Sheet Metal Fabrication
-

Axis High Precision CNC Machining Parts
-

CNC Machined Parts for Italy
-

CNC Machining Aluminum Parts
-

Auto Parts Machining
-

Titanium Alloy Forgings
-

Titanium and Titanium Alloy Fittings
-

Titanium and Titanium Alloy Forgings
-

Titanium and Titanium Alloy Wires
-

Titanium Bars
-

Titanium Seamless Pipes/Tubes
-

Titanium Welded Pipes/Tubes