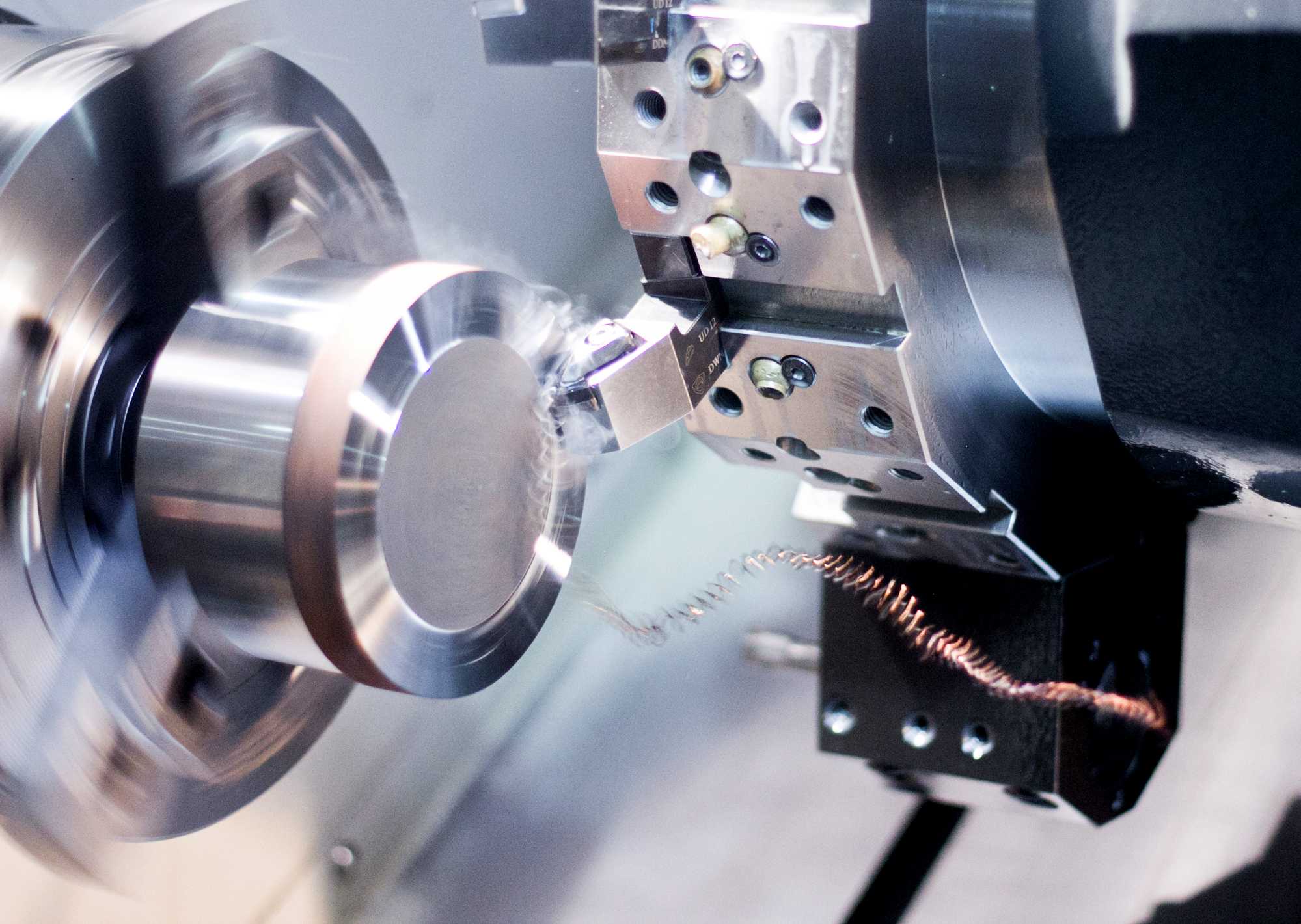
Precision machining is a critical process in the manufacturing industry, and the use of different materials adds complexity and diversity to the production of precision machining parts. From metals to plastics, the range of materials used in precision machining is vast, and each material presents its own set of challenges and opportunities for manufacturers. Metals are commonly used in precision machining due to their strength, durability, and heat resistance. Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and brass are just a few examples of metals that are frequently machined to create precision parts. Each metal requires specific machining techniques and tools to achieve the desired precision and finish. For instance, stainless steel is known for its hardness and toughness, requiring specialized cutting tools and coolant systems to prevent overheating and maintain accuracy during machining.
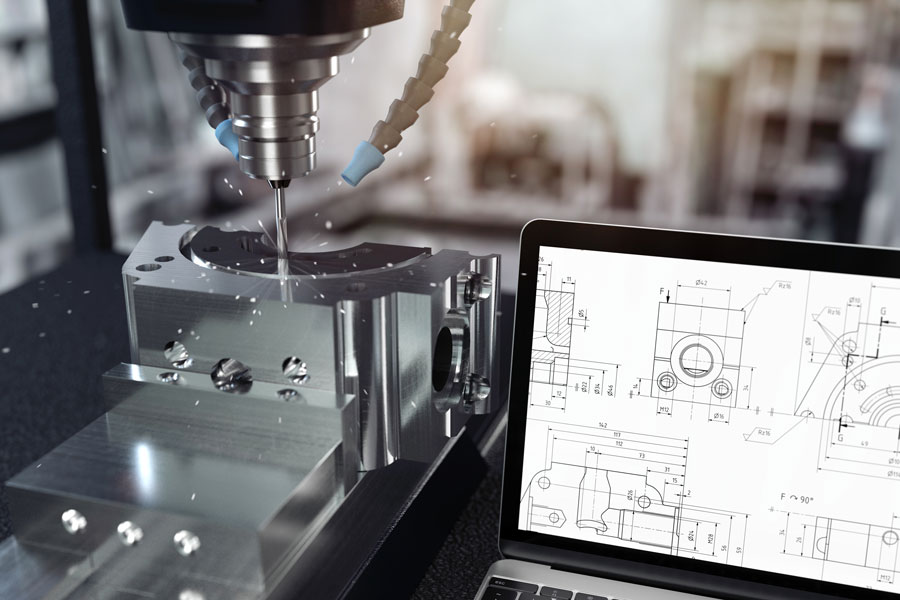
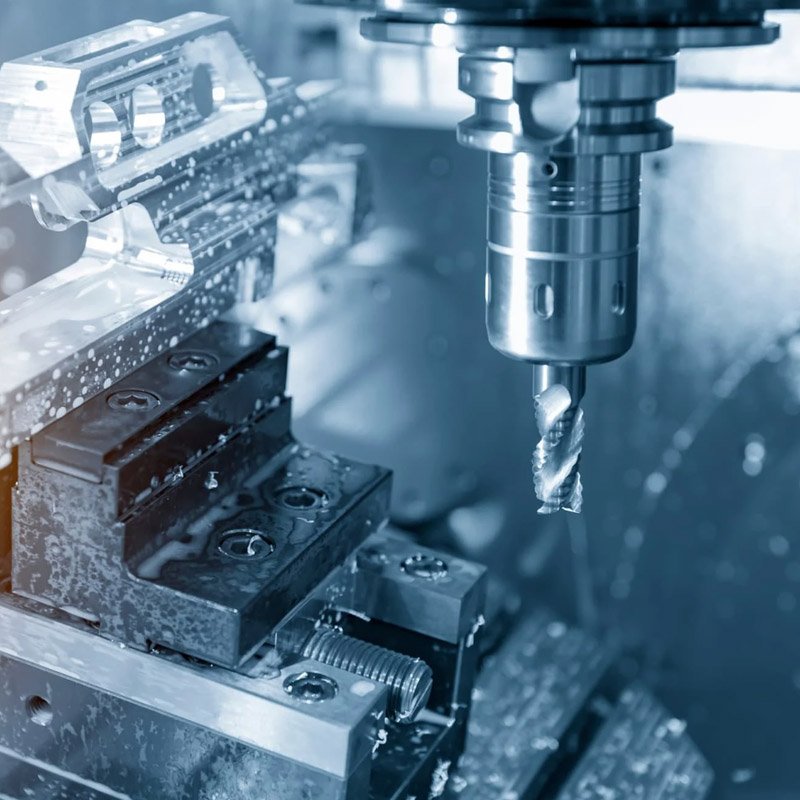


In addition to metals, plastics are also widely used in precision machining. Materials such as nylon, polycarbonate, and acrylic offer unique properties such as flexibility, transparency, and chemical resistance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Machining plastics requires careful consideration of factors such as heat generation, tool selection, and chip control to avoid melting or warping of the material. Furthermore, the use of composite materials in precision machining has gained popularity in recent years. Composites, which are made by combining two or more materials to create a new material with enhanced properties, offer a lightweight and high-strength alternative to traditional metals. Carbon fiber, fiberglass, and Kevlar are examples of composites that are machined to produce precision parts for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.
The selection of the right material for precision machining depends on the specific requirements of the part, including mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate the characteristics of each material and tailor their machining processes to achieve the desired outcome. In addition to material selection, precision machining also involves the use of advanced technologies such as computer numerical control (CNC) machining, multi-axis milling, and electrical discharge machining (EDM). These technologies enable manufacturers to achieve high levels of precision and repeatability in the production of complex parts, regardless of the material being machined.
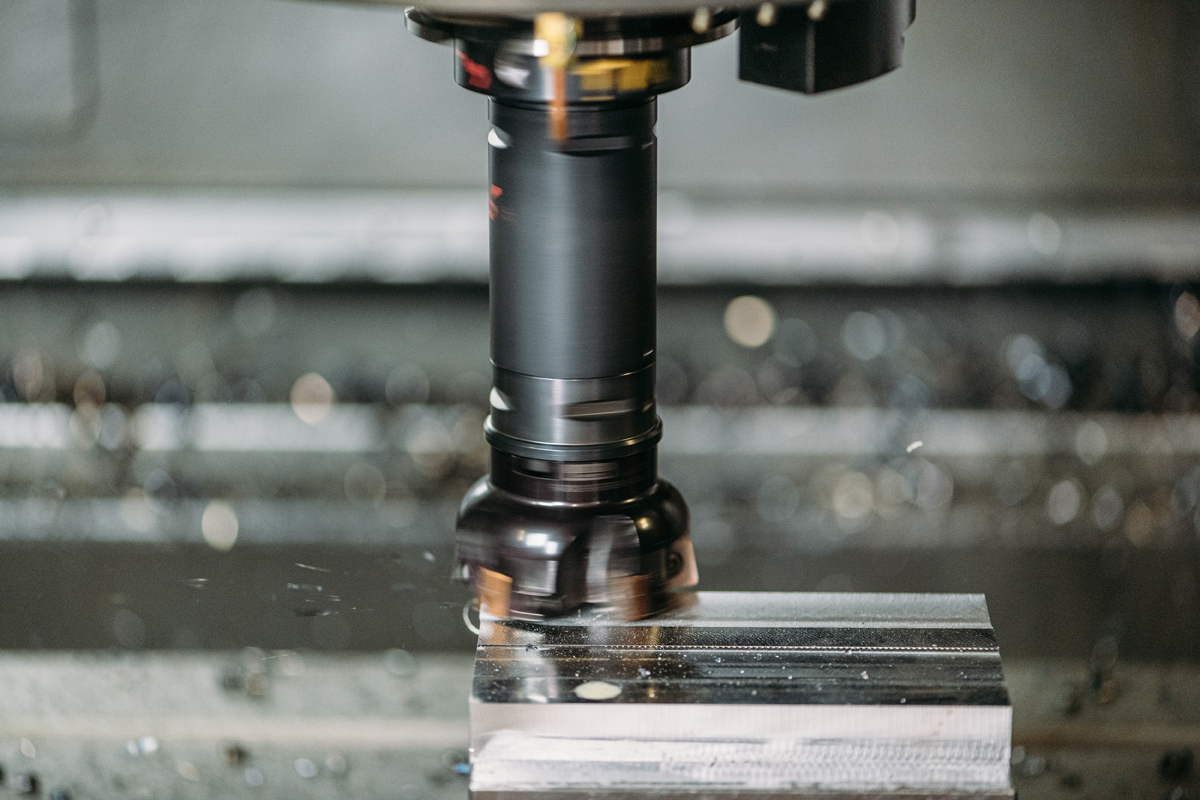

The demand for precision machining parts with different materials continues to grow as industries seek to improve the performance and efficiency of their products. Whether it's producing intricate components for medical devices or creating durable parts for industrial machinery, the ability to machine a diverse range of materials with precision is essential for meeting the evolving needs of the market. As the manufacturing landscape evolves, the development of new materials and machining techniques will further expand the possibilities for precision machining. Innovations in additive manufacturing, nanomaterials, and hybrid machining processes are poised to revolutionize the way precision parts are produced, opening up new opportunities for manufacturers to push the boundaries of what is possible in the world of precision machining.
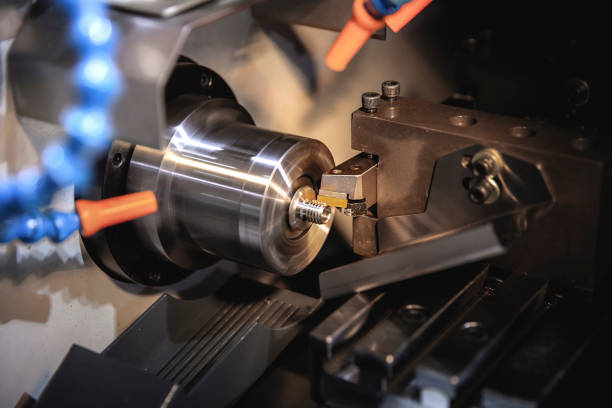
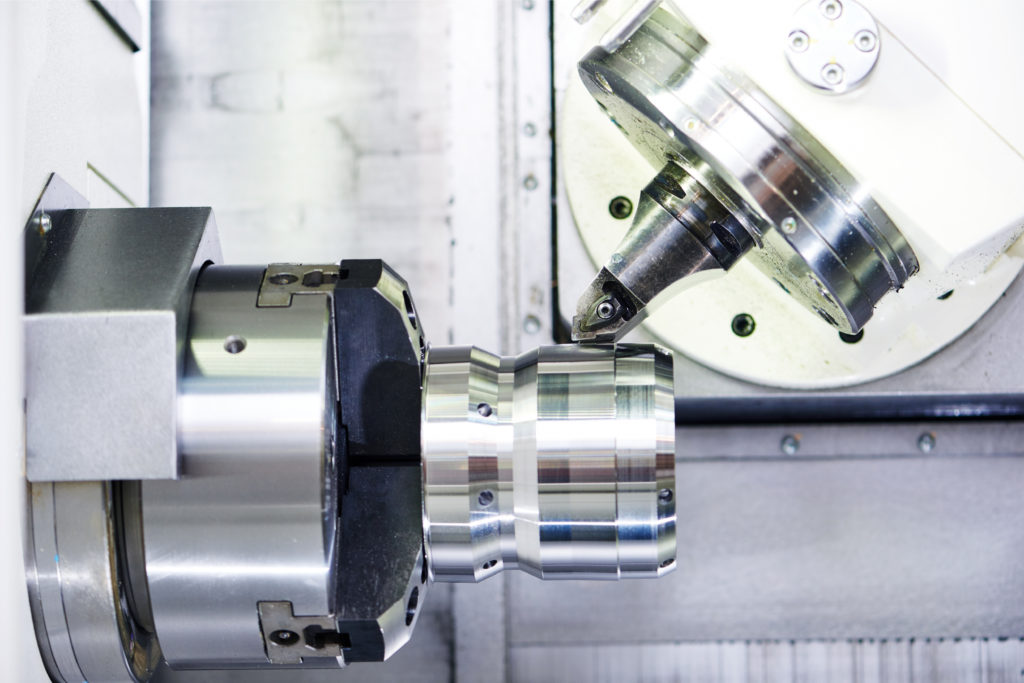


In conclusion, precision machining parts with different materials is a complex and dynamic field that requires expertise, innovation, and adaptability. The ability to work with a variety of materials, from metals to composites to plastics, is essential for manufacturers to meet the diverse needs of modern industries. With the right combination of materials, technologies, and skills, precision machining will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Post time: Aug-12-2024
