
Pulse and Continuous Wave Modes
An important part of optical micromachining is the transfer of heat to the area of the substrate adjacent to the micro-machined material. Lasers can operate in pulsed mode or continuous wave mode. In continuous wave mode, the laser output is substantially constant over time.


In pulsed mode, the laser output is concentrated in small pulses. Pulsed mode laser devices provide pulses and small pulse durations with sufficient energy for micromachining of a given material. Small pulse duration minimizes heat flow to surrounding material. Laser pulses can vary in length from milliseconds to femtoseconds.
The peak power is related to the duration of the laser pulse, so pulsed lasers can achieve much higher peaks than continuous waves.
Laser processing primarily involves interactions that lead to ablation of the substrate material. The energy transfer that occurs depends on the material and laser properties. Laser characteristics that are influencing factors include peak power, pulse width, and emission wavelength. A material consideration is whether it can absorb laser energy through thermal and/or photochemical processes.
Why is the pulse width important?
Laser cutting is clean and precise. The need to make smaller, faster, lighter and lower cost devices requires lasers to meet the challenge. Pulsed lasers are used for precision micromachining of various materials. The ability to generate different pulse widths is the key to accuracy, throughput, quality and cost-effectiveness.
Nanosecond lasers use the same average power with higher material removal rates and therefore higher throughput than picosecond and femtosecond lasers.
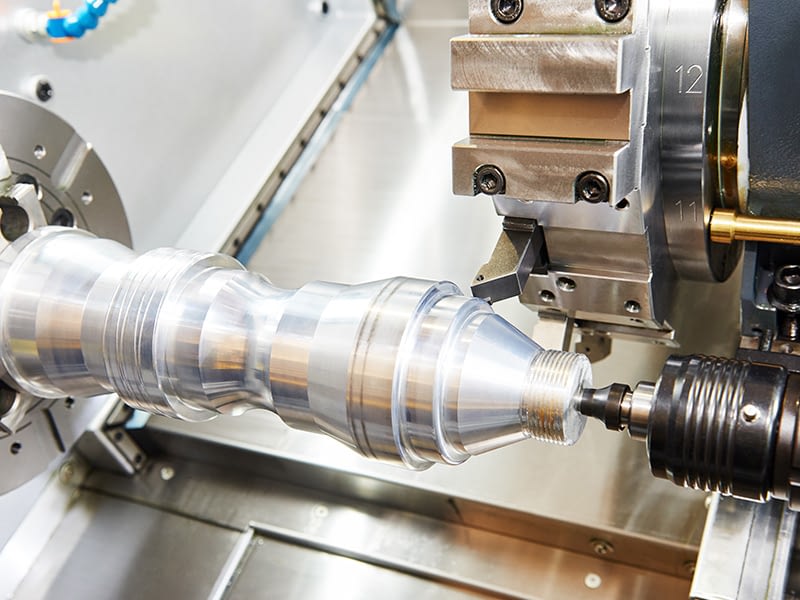


Picosecond and femtosecond lasers melt material to remove it through a process of vaporizing and melting the material to expel it. This melting can affect the precision and quality of machining, as the removed material can adhere to the edges and resolidify.
Advances in pulsed laser technology have made it possible to use micromachining on tiny devices, such as medical devices, with minimal damage to surrounding materials. With rapid scientific progress in the field of lasers, laser micromachining expertise is critical.
The production process of a machine refers to the entire process of making a product from raw materials (or semi-finished products). For machine production, it includes the transportation and storage of raw materials, production preparation, blank manufacturing, parts processing and heat treatment, product assembly, and debugging, painting and packaging, etc. The content of the production process is very extensive. Modern enterprises use the principles and methods of systems engineering to organize and guide production, and regard the production process as a production system with input and output.

Post time: Oct-13-2022
